HEMORRHOIDS (PILES)
What are hemorrhoids?
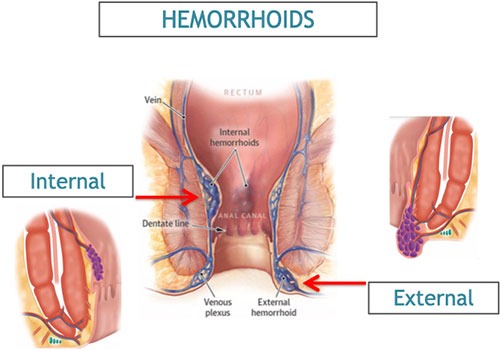
Hemorrhoids are swollen veins in the lower rectum and anus. The anus is at the end of the rectum and is the opening through which bowel movements pass from your body. Hemorrhoids are a common problem. Another name for them is piles.
Hemorrhoids may be inside the rectum (internal) or around the anus (external). Internal hemorrhoids are often painless, but sometimes cause a lot of bleeding. The internal veins may stretch and even fall down (prolapse) through the anus to outside the body. The veins may then become irritated and painful. External hemorrhoids can be seen or felt easily around the anal opening. When the swollen veins are scratched or broken by straining, rubbing, or wiping, they sometimes bleed.
How do hemorrhoids occur?

Veins in the rectum and around the anus tend to swell under pressure. Hemorrhoids can result from too much pressure on these veins. You may put pressure on these veins by:
- straining to have a bowel movement when you are constipated
- waiting too long to have a bowel movement
- sitting for a long time on the toilet, which causes strain on the anal area
- coughing and sneezing often
- sitting for a long while.
Hemorrhoids may also develop from:
- diarrhea
- obesity
- injury to the anus, for example, from anal intercourse
- some liver diseases.
Flare-ups of hemorrhoids may occur during periods of stress. Some people inherit a tendency to have hemorrhoids.
Pregnant women should try to avoid becoming constipated because they are more likely to have hemorrhoids during pregnancy. In the last trimester of pregnancy, the enlarged uterus may press on blood vessels and cause hemorrhoids. Also, the strain of childbirth sometimes causes hemorrhoids after the birth.
What are the symptoms of hemorrhoids?

Symptoms of hemorrhoids include:
- itching, mild burning, and bleeding around the anus (for example, you might see bright red blood on toilet paper after wiping)
- swelling and tenderness around the anus
- pain with bowel movements
- painful lumps around the anus ranging in size from a pea to a walnut (in severe cases).
What are the degrees (grades) of hemorrhoids?
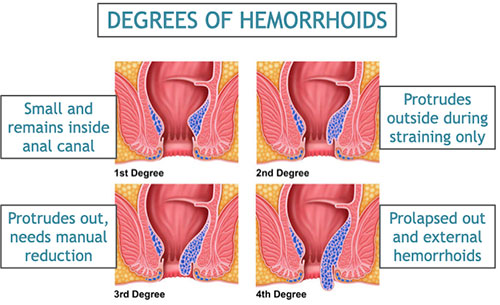
Hemorrhoids that are small and remain inside the anal canal are called Grade 1 piles. Those that protrude outside while straining for defecation and then reduce spontaneously are Grade 2. Those are protrude out but need to be manually reduced are Grade 3. Piles that stay prolapsed out and external haemorrhoids are Grade 4. These can be further complicated by being thrombosed (blood clot inside the vein) or gangrenous (dead tissue due to loss of blood supply).
How are hemorrhoids diagnosed?
Your health care provider will examine your rectum and anus. Your provider may use a special light tool called a proctoscope or anoscope to look inside the rectum. This is an office or clinic procedure which is quick and usually painless. In certain cases, your doctor may advise an endoscopy of your intestines to rules out certain diseases.
What is the treatment of hemorrhoids?
Hemorrhoids can be treated by either one or a combination of the following methods:
- Diet and lifestyle modification: high fibre diet, fluids, sitz bath and cold packs etc.
- Medications: oral medications, local creams, suppositories etc.
- Non-surgical procedures: rubber band ligation, injection sclerotherapy etc.
- Surgery: Lasers ablation, arterial ligation, conventional or stapled hemorrhoid surgery etc.
What are the diet and lifestyle modifications for treatment of hemorrhoids?
It is recommended to eat more high-fibre foods, which will help prevent constipation. Good sources of fibre include fresh fruit, raw or cooked vegetables, especially asparagus, cabbage, carrots, corn, and broccoli, and whole-grain cereals with bran, such as shredded wheat or bran flakes. Drink plenty of water. This helps to soften stools so they are easier to pass. Regular exercise and sleep patterns also helps constipation. It is important to follow the urge of defecation and avoid straining or sitting for too long during defecation. Avoiding junk and processed foods, flour, alcohol, spices, caffeine etc as much as possible definitely helps regular bowel movements. Sitz bath (sitting in lukewarm water) 2 or 3 times a day for 15 minutes cleans the anal area and may relieve discomfort. Also, you might try putting a cloth-covered ice pack on the anus for 10 minutes, 4 times a day.
What is the medical treatment of hemorrhoids?
For mild discomfort, your health care provider may prescribe a cream or ointment for the painful area. Your provider may also prescribe medicated suppositories to put inside the rectum. In case of bleeding or large piles, you may need oral medications (e.g. flavonoids) as well. Constipation may need stool softeners, fibre supplements, mild laxatives etc.
What are the non-surgical procedures for treatment of hemorrhoids?
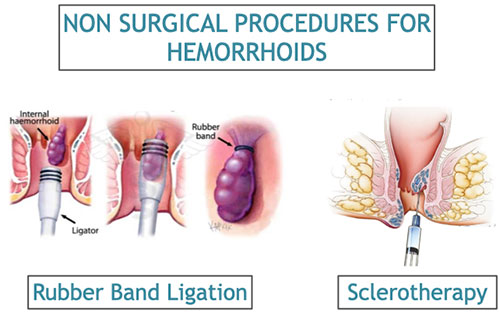
A number of procedures can be used to remove or shrink hemorrhoids. These are all office, clinic or short stay procedures and suitable for smaller piles, usually grade 1 and 2, not responding to medical treatment alone. If you have protruding internal hemorrhoids, your health care provider can do a procedure called hemorrhoid banding. Your provider will put a tight band around the enlarged vein and either cut the hemorrhoid open, remove any blood clots, and let the vein heal, or let the hemorrhoid dry up and fall off. This method is effective in most cases. Other methods include destroying the hemorrhoid with freezing, electrical or laser heat, or infrared light. Or your provider may shrink the hemorrhoid by injecting a chemical in or around the swollen vein, a procedure called sclerotherapy.
What are the surgical options for treatment of hemorrhoids?

A number of surgical procedures can be offered for larger hemorrhoids (Grade 3 and 4), for smaller piles not responding to other modalities of treatment. Conventionally hemorrhoids have been treated by a procedure called hemorrhoidectomy i.e. excision and removal of hemorrhoids). This can be an open hemorrhoidectomy when the raw wounds are kept open and allowed to heal over a few weeks, or a closed hemorrhoidectomy when these raw wound defects are closed with stitches, thereby reducing the healing time and pain after surgery. There is another method which uses a stapler to divide and seal the blood vessels in the up anorectal region, thereby avoiding an external wound. This is called stapled hemorrhoidectomy

Laser hemorrhoidectomy has revolutionised the surgical management of hemorrhoids. Most hemorrhoids requiring surgery can be tackled with these state-of the art laser fibres that enter the pile mass through tiny punctures and thermally ablate the swollen blood vessels, causing them to shrink and reduce in size dramatically. These have the added benefit of minimal pain and wound issues, shorter hospital stays, earlier return to work and normal activities.
How can I take care of myself from hemorrhoids?
Always tell your health care provider when you have rectal bleeding. Although bleeding may result from hemorrhoids, more serious illnesses, such as colon cancer, can also cause bleeding.
Follow these guidelines to help prevent hemorrhoids and to relieve their discomfort:
- Do not strain during bowel movements. The straining makes hemorrhoids swell.
- Follow your high-fibre diet and drink plenty of water. If necessary, take a stool softener. Softer stools make it easier to empty the bowels and reduce pressure on the veins.
- Don't overuse laxatives. Diarrhea can be as irritating to the anus as constipation.
- Ask your health care provider what non-prescription product you should buy to relieve pain and itching. Also, ask about any side effects of any medications prescribed for you.
- Exercise regularly to help prevent constipation.
- Avoid a lot of wiping after a bowel movement if you have hemorrhoids. The best option to clean the area is water. If not available, wiping with soft, moist toilet paper (or a commercial moist pad or baby wipe) may relieve discomfort.
- Avoid lifting heavy objects when you have hemorrhoids. It may increase the pressure on the veins and make the hemorrhoids worse.